Intensity-guided edge-preserving depth upsampling through weighted L0 gradient minimization
Cheolkon Jung1 Shengtao Yu1 Joongkyu Kim2
1Xidian University
2Sungkyunkwan University
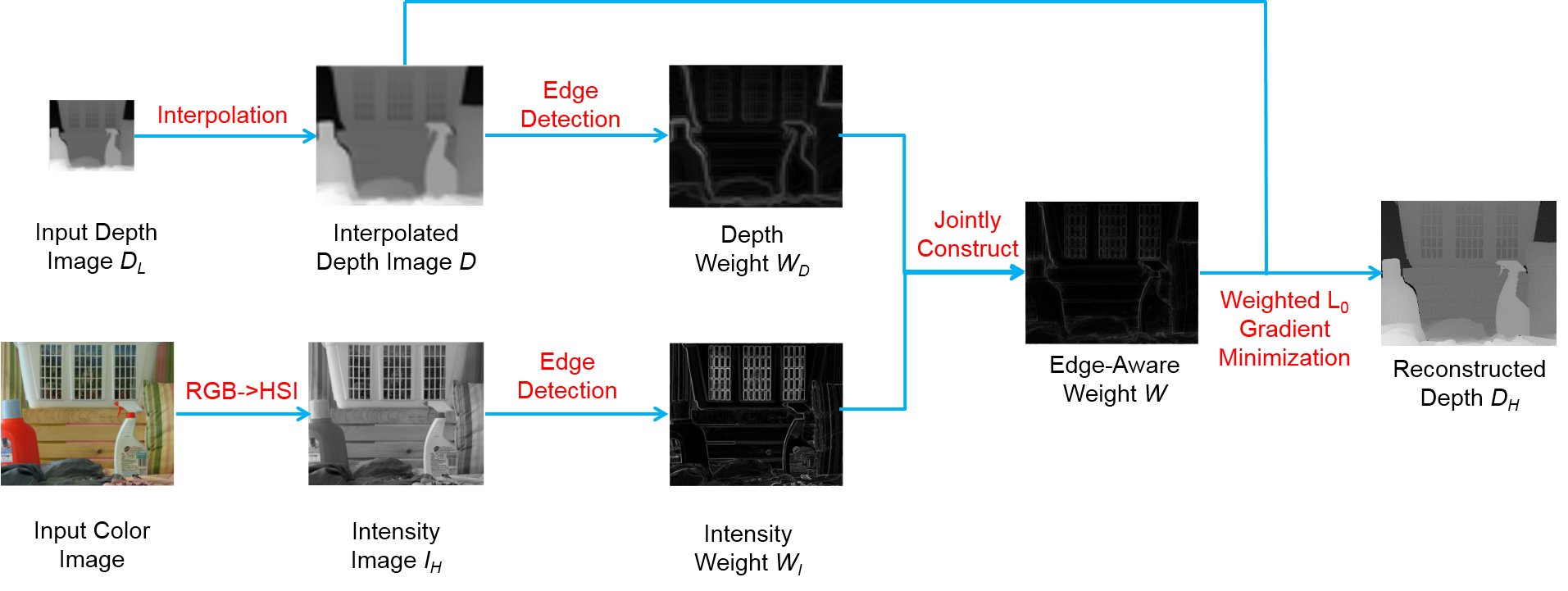
Fig. 1. Framework of the proposed method
Abstract
Depth is an important visual cue to perceive real-world scenes. Although a time-of-flight (ToF) depth camera can provide depth information in dynamic scenes, captured depth images are often noisy and of low resolution. In this paper, we propose an intensity-guided edge-preserving depth upsampling method through weighted L0 gradient minimization to enhance both resolution and visual quality of depth images. Guided by the high-resolution intensity image, we perform optimization to preserve boundaries of objects. We apply L0 gradient to the regularization term, and compute its weight from both intensity and depth images. We optimize the objective function using alternating minimization and half-quadratic splitting. Experimental results on Middlebury 2005, 2014, and real-world scene datasets demonstrate that the proposed method produces boundary-preserving depth upsampling results and outperforms state-of-the-art ones in terms of accuracy.
Paper
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvcir.2016.11.009
Citation:
Cheolkon Jung, Shengtao Yu, Joongkyu Kim, “Intensity-Guided Edge-Preserving Depth Upsampling through Weighted L0 Gradient Minimization,” Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, vol. 42, pp. 132-144, 2017
Test Images: Download
Executable Files: Download
Results





(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)





(f)
(g)
(h)
(i)
(j)
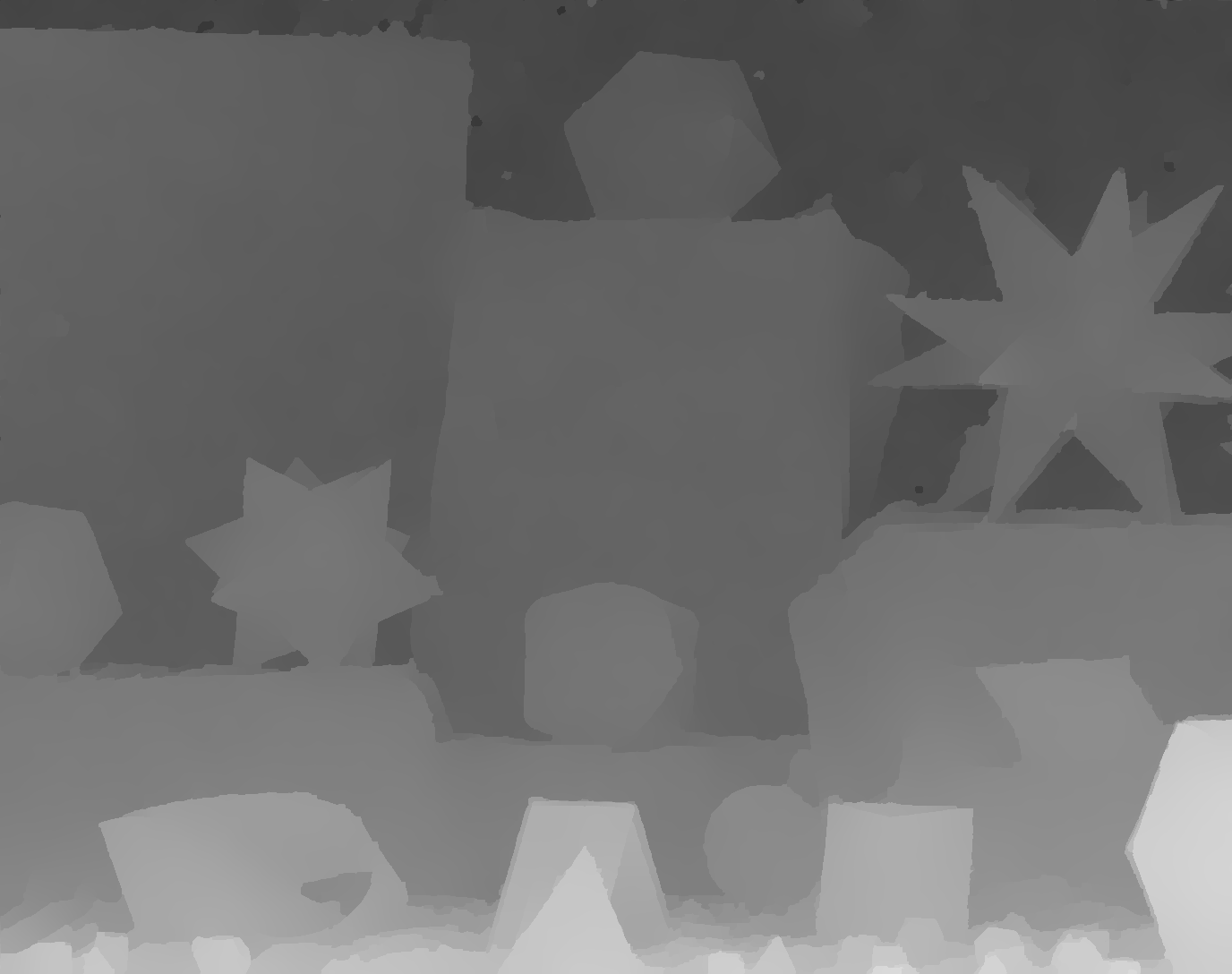
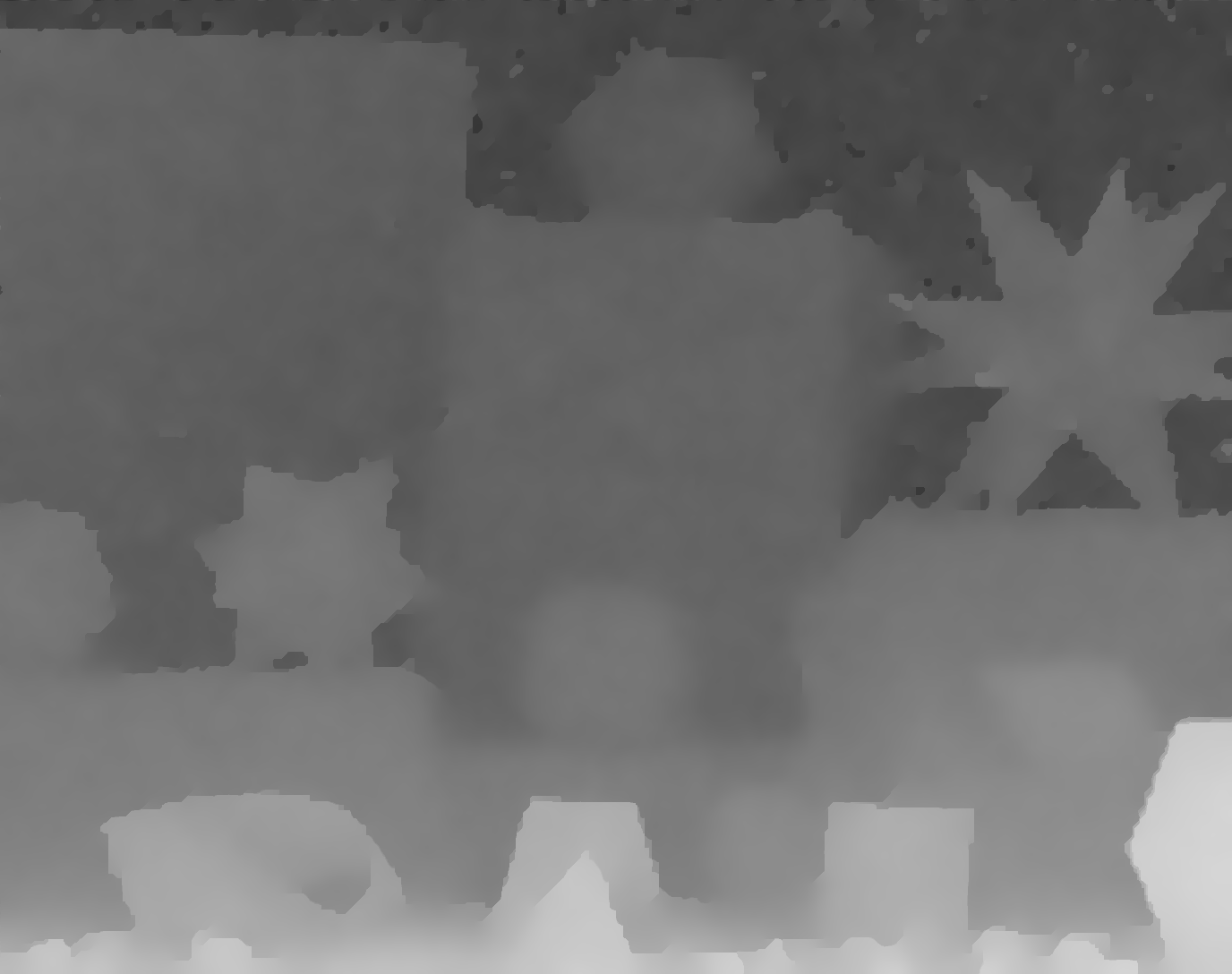





(k)
(l)
(m)
(n)
(o)
Fig. 2. Visual comparison of x8 upsampling on the Middlebury 2005 Moebius dataset. (a) Color image. (b) LR depth image (enlarged using nearest interpolation). (c) Bilinear interpolation. (d) Yang et al. [1]. (e) He et al. [2]. (f) Diebel and Thrun [3]. (g) Chan et al. [4]. (h) Park et al. [5]. (i) Liu et al. [6]. (j) Ferstl et al. [7]. (k) L0 gradient minimization with constant weight. (l) L0 gradient minimization with intensity weight. (m) L0 gradient minimization with depth weight. (n) Proposed. (o) Ground truth.
Reference
[1] Q. Yang, R. Yang, J. Davis, and D. Nister, “Spatial-depth super resolution for range images,” Proc. IEEE CVPR, 2007, pp. 1–8.
[2] K. He, J. Sun, and X. Tang, “Guided image filtering,” IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., vol. 35, no. 6, pp. 1397–1409, Jun. 2013.
[3] J. Diebel and S. Thrun, “An application of Markov random fields to range sensing,” in Proc. NIPS, 2005, pp. 291–298.
[4] D. Chan, H. Buisman, C. Theobalt, and S. Thrun, “A noise-aware filter for real-time depth upsampling,” in Proc. ECCV Workshop, 2008, pp. 1–12.
[5] J. Park, H. Kim, Y.-W. Tai, M. S. Brown, and I. Kweon, “High quality depth map upsampling for 3D-TOF cameras,” in Proc. IEEE ICCV, 2011, pp. 1623–1630.
[6] M.-Y. Liu, O. Tuzel, and Y. Taguchi, “Joint geodesic upsampling of depth images,” in Proc. IEEE CVPR, 2013, pp. 169–176.
[7] D. Ferstl, C. Reinbacher, R. Ranftl, M. Rüther, and H. Bischof, “Image guided depth upsampling using anisotropic total generalized variation,” in Proc. IEEE ICCV, 2013, pp. 993–1000.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61271298) and the International S&T Cooperation Program of China (No. 2014DFG12780).